Web Computer Graphics (Part 1)
Categories: Study
Preface
Answer from vczh to a computer graphics question:
Programmer’s three major romances: operating system, graphics, compilation principle. Learning them is to broaden your horizons. These are not courses that you will be doomed if you don’t learn, but if you want to become a master, you have to learn =_,=
Web front-end technologies related to graphics are roughly CSS3 animation transformation, SVG, Canvas, WebGL. However, front-end engineers mostly only stay at the upper-level API operation aspect. They may not know much about the principles of graphics, such as GPU, image representation, image geometric transformation principles, texture, hierarchical models, etc.
After sorting out SVG New Driver’s Guide, I have some interest in some underlying technologies. Plus this piece belongs to a blank area, so I spent a few days learning graphics basically and recorded it here.
This article mainly includes the following contents:
GPU
Concept and History
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a microprocessor specially designed to run drawing calculation work on personal computers, workstations, game consoles and some mobile devices.
GPU related concepts were proposed in the late 1970s, using monolithic integrated circuits as graphics chips. At that time, they were already used in video, games, and animation, and could quickly synthesize several pictures (only this function…);
By the late 1980s, GPUs based on digital signal processor chips were developed. Compared with previous generations, they were faster and more functional, but very expensive;
By 1998, NVIDIA announced the successful development of modern GPU, marking the historic breakthrough of GPU R&D becoming a reality. Modern GPU uses transistors for calculation. In microchips, the transistors used by GPU have far exceeded CPU.
After that, generations of modern GPUs were developed, and functions and running speeds were constantly enhanced.
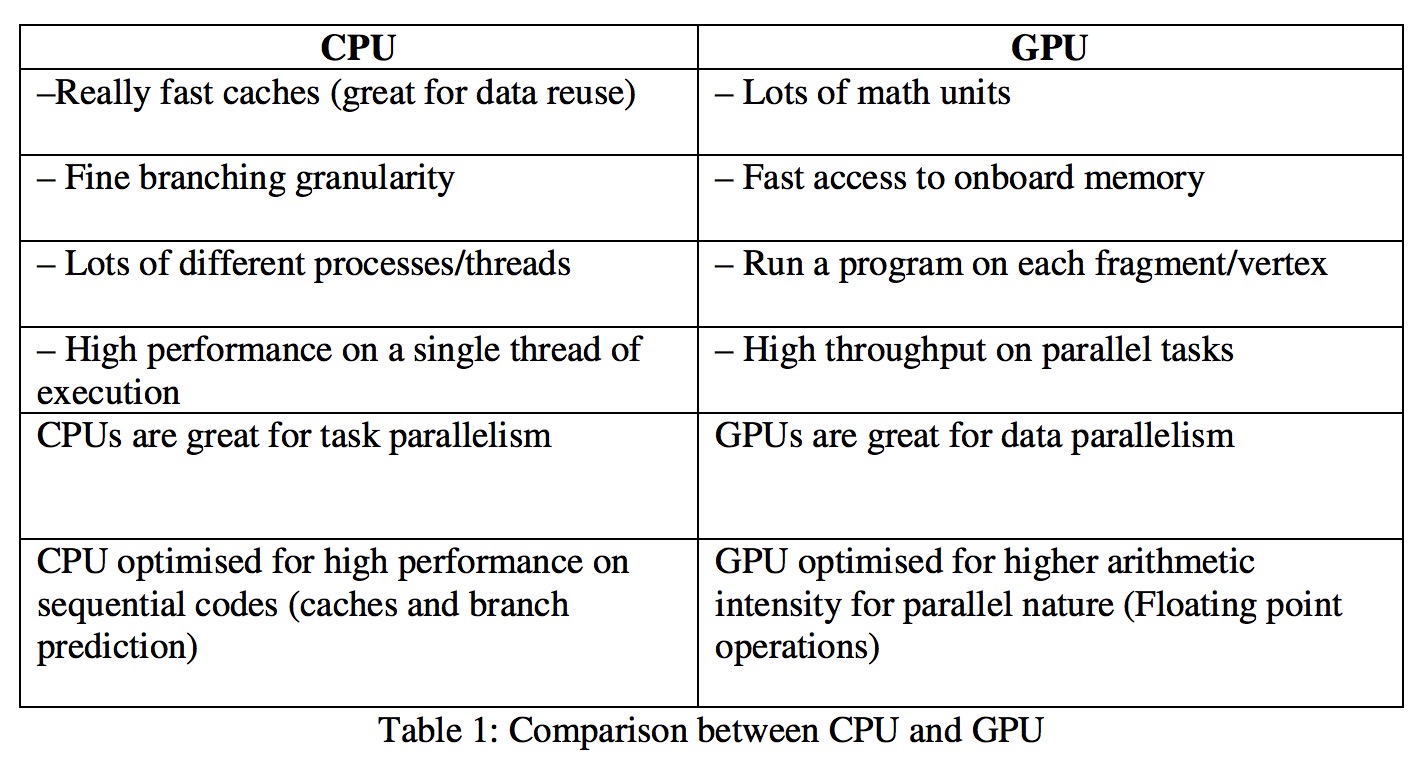
GPU VS CPU
Someone may ask, we already have CPU to interpret computer instructions and process data in computer software, why use GPU? To explain this, we can start from the structure of CPU and GPU.
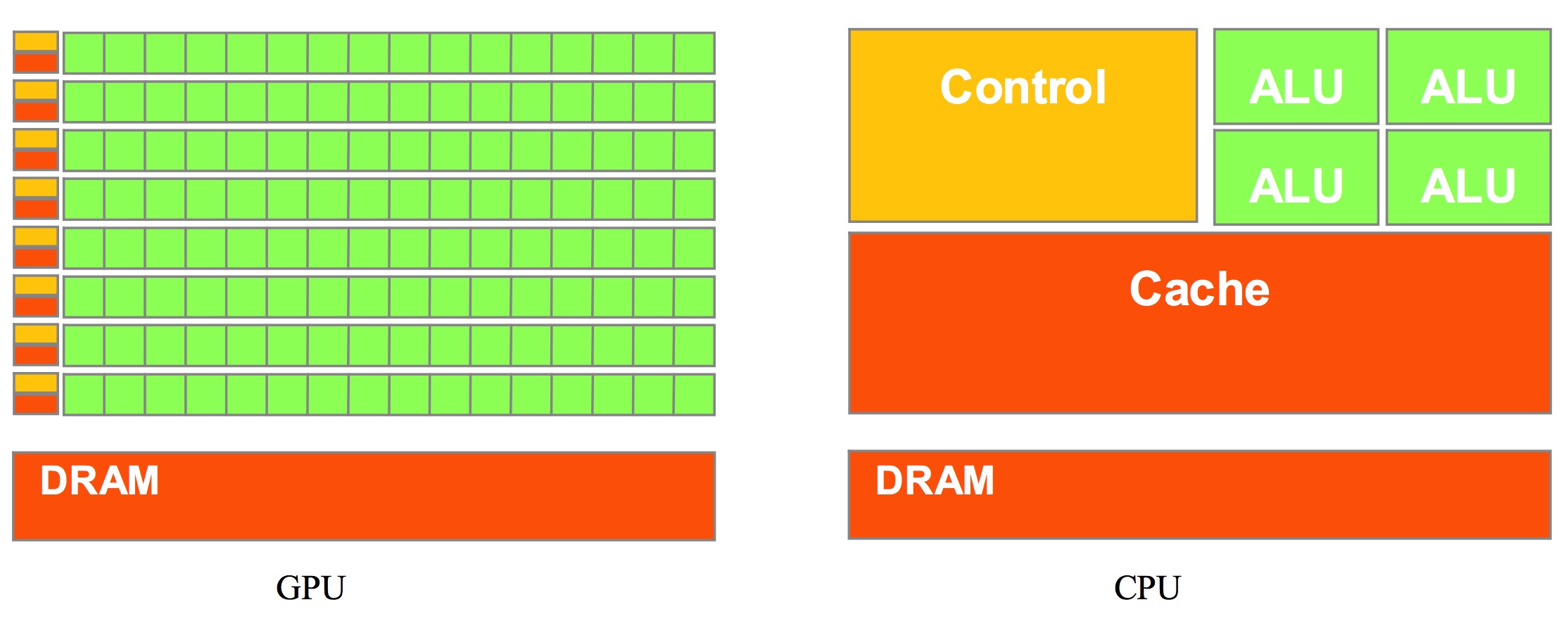
Picture from NVIDIA CUDA document. Green ones are computing units, orange-red ones are storage units, orange-yellow ones are control units.
From the above figure, we can see that GPU is designed based on large throughput, adopting a large number of computing units and ultra-long pipelines, but only very simple control logic and omitting Cache. It has great advantages in computing-intensive programs and easy-to-parallel program running;
CPU is based on low-latency design, has powerful ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). Structurally, not only Cache occupies a large amount of space, but also has complex control logic and many optimized circuits. In contrast, computing power is only a small part of CPU.
The abbreviation of CPU is Central Processing Unit, GPU is Graphics Processing Unit. Superficially can be understood as one is a bus driver, the other is a special car driver. But actually GPU work technical content is lower than CPU, used for large calculation volume, lower technical content compared to CPU, repeated many times work. Someone compared CPU to an old professor, and GPU to a primary school student. Professor’s ability to handle complex tasks crushes primary school students, but for tasks not so complex, still can’t withstand many people (A flavor of blacking…
Summarized like this:
Hardware Acceleration in Front-end
Regarding hardware acceleration in front-end, it is actually creating a Composited Layer to enable GPU hardware acceleration, rendering via GPU, liberating CPU. Creating Composited Layer specifically has the following methods:
- 3D or perspective transform CSS property.
- Hybrid plugin (such as Flash)
- Element doing CSS animation on its own opacity or using an animated webkit transform
- Element has accelerated CSS filters
- Element has a descendant node containing a composite layer (in other words, an element has a child element, the child element is in its own layer)
- Element has a sibling element with a lower z-index and containing a composite layer (in other words, the element is rendered on top of the composite layer)
In chrome, you can open Composited Layer like this:
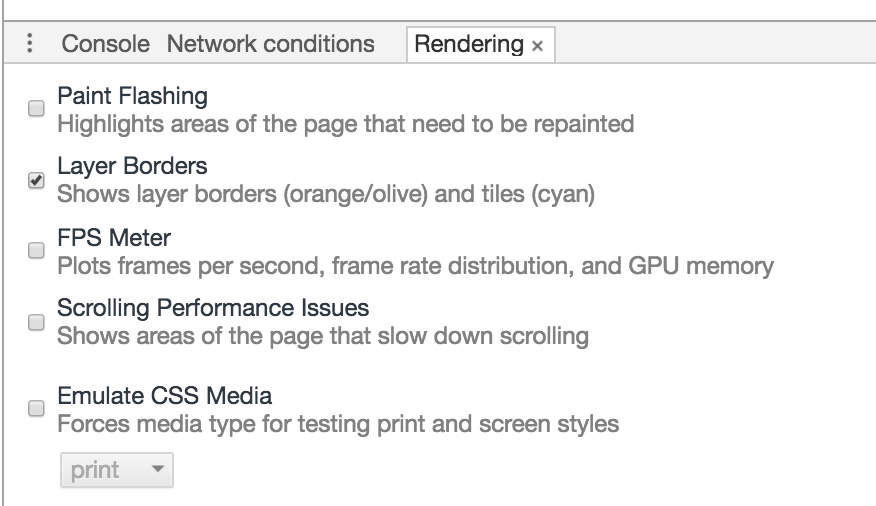
Image Representation
Introduction
What is computer graphics? On Computer graphics (disambiguation) it says:
Computer graphics are graphics created by computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of pictorial data by a computer.
That is, computer graphics are graphics created by computers, and more generally, the representation and manipulation of graphical data by computers.
In this chapter, mainly clarify how pictures are represented by data and specific data formats, and explain how colors are represented in computers?
Suppose we want to save the beautiful scenery we see, usually take it as a photo. Considering storage cost, we must convert it into a finite size digital form analog signal. This conversion process is sampling. Sampling theory is also a relatively important content in GC. Discuss in detail when have time.
The information we see in photos will definitely be much smaller than the information contained in real scenes, and will not be infinite width and height like in reality. Thus we must compromise on accuracy, sampling and storing our images by choosing appropriate methods.
Raster Image Representation
Computer graphics solves the problem of image representation by dividing the image (picture) into a regular grid, which we call raster. Each grid cell is a “picture element”, a term often contracted with pixel. Pixel is the atomic unit of image, that is, a single color body.
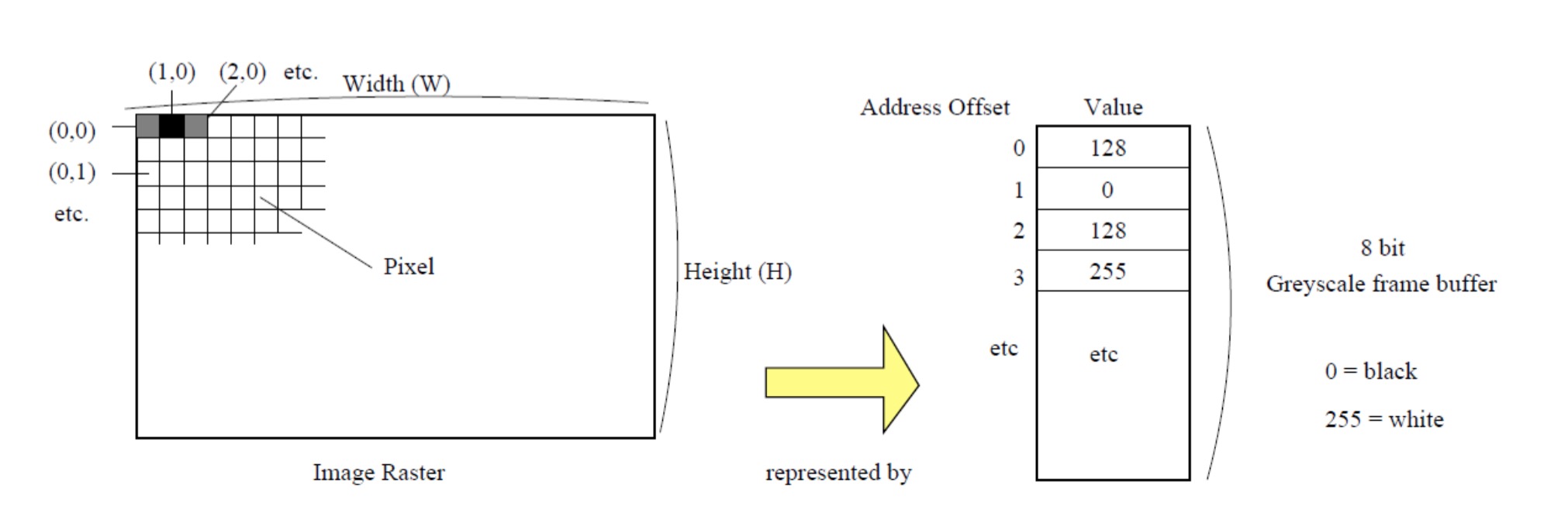
Above, representing digital image via raster. Raster indicates here is a gray image, its content represents grayscale frame buffer in memory. Values stored in frame buffer record the intensity of pixels on a discrete scale (0 = black, 255 = white).
The screen resolution we usually talk about is the number of pixels in the image. The greater the resolution, the greater the spatial detail of the image.
Frame Buffer
We use a structured method to store the color value of each pixel to represent an image.
Frame buffer initially defined as memory reserved to directly manipulate currently displayed image. in early graphics, special hardware was needed to store enough data to represent just a single image. But now we can manipulate hundreds or thousands of pictures in memory at the same time, thus “frame buffer” gradually used to describe any block of storage representing an image.
Common frame buffers now include grayscale frame buffer, pseudo-color frame buffer, true color frame buffer these three.
Grayscale frame buffer is one of the simplest forms, encoding pixels by using various gray gradients. Use 8 bits to encode pixel as unsigned integer, representing 256 different gray shades.
Pseudo-color frame buffer is a storage scheme same as grayscale frame, but can be used to represent color images, i.e. each of 0-255 represents a specific color, rather than representing gray shade.
True color frame buffer is also used to represent color images, but not representing color via lookup table like pseudo-color frame buffer, but directly storing RGB color value of each pixel in frame buffer. If we use 8 bits (1 byte) to represent red, green and blue specific colors, then each pixel will need 24 bits (3 bytes) of storage space.
Color Representation
To figure out color, we can first understand our eyes.
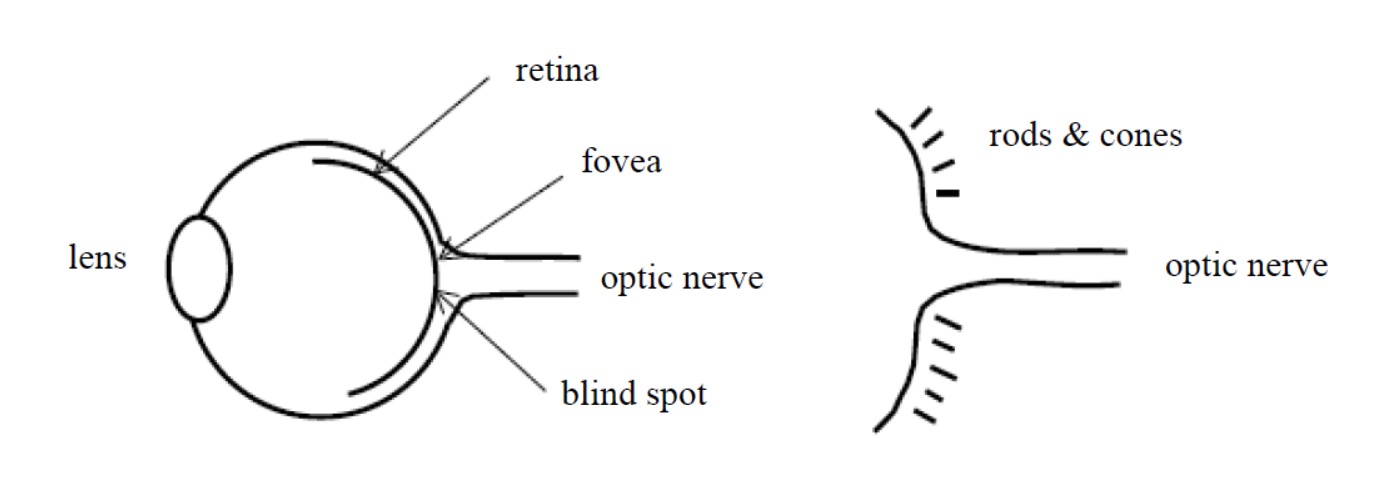
Looking at the picture and speaking is like this:
- lens: elastic lens, our eyes focus light onto retina through it;
- retina: retina, fovea in retina is the part with highest visual acuity in retina, is concentration area of rods cells and cones cells. These two special cells (rod and cone) can convert light information into electrical impulses;
- optic nerve: optic nerve, light information converted into electrical impulses transmitted to our brain via optic nerve;
- blind spot: blind spot, place without photoreceptor cells;
cones cone cells responsible for color vision, it has three types of cones, all have developed to have high sensitivity to light of specific wavelengths (blue, green, red).

Red, green and blue are called “additive primary colors”, other colors can be obtained by superimposing different amounts of red, green and blue light.
RGB Color Representation
In the figure above we can see Red+Green=Yellow. In front-end representing color usually uses HEX method or RGB method. Yellow is represented as #FFFF00 or rgb(255,255,0). So why can we see yellow? We can understand it as, that yellow object actually dislikes yellow the most, it absorbed other lights, reflected yellow out, thus yellow narrow band light wave entered our eyes, stimulated red and green cone cells, so we feel the object is yellow.
rgba representing color is also relatively common in front-end. It is an extension of RGB color model. This abbreviation stands for initials of red green blue three primary colors. Alpha value represents color transparency/opacity, value range 0-1.
HSL Color Representation
Besides using RBG to represent color, can also use three elements of color to represent, i.e. HSL color representation, which includes follows:
- Hue: hue, refers to the appearance of color, is different colors felt by human eyes under irradiation of light of different wavelengths, such as red, yellow, blue etc. These colors are distributed on a plane hue ring, value range is 0° to 360° central angle, each angle can represent a color.
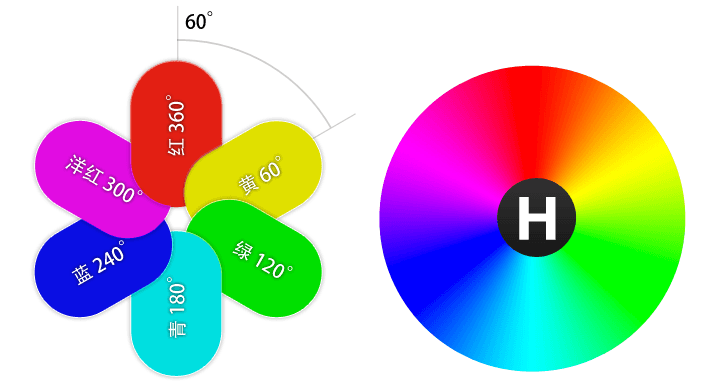
- Saturation: saturation, refers to purity of color, higher means purer color, lower means gradually becoming gray.

- Lightness: lightness, also called brightness, refers to lightness and darkness of color.

Also has hsla, can compare with rgba above.
Quick switch between RGB and HSL can be achieved via chrome, hold shift then click to switch.
In addition, there is HSV to represent color, i.e. Hue, Saturation, Value, also called HSB, where B is English: Brightness.
Geometric Transformation
Geometric transformation is related to transform in CSS3. This section mainly gives transform principle from mathematics aspect.
Geometric transformation is sometimes also called rigid body transformation, i.e. all points in graphics are carried out under the same transformation. Can distinguish whether it is rigid body transformation from the figure below:

Among them Fig 2 obtained by reflection of Fig 1, Fig 3 obtained by scaling and rotation combination of Fig 1, then Fig 4 is obtained by pin-cushion distortion non-rigid body transformation of Fig 1. Please note, only rigid body transformation can be implemented using matrix multiplication.
First we can review matrix multiplication in linear algebra:
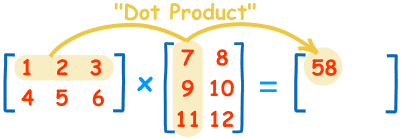
The value at the intersection of m-th row and n-th column of result matrix is equal to the sum of products of each value at corresponding position of m-th row of first matrix and n-th column of second matrix. At the same time it is only meaningful when the number of columns of the first matrix is same as the number of rows of the second matrix.
Following examples are all told using two-dimensional rigid body graphic transformation.
Two-dimensional Rigid Body Transformation
Scale
We can use the following scaling matrix to process scaling of a two-dimensional graphic:
 Where Sx and Sy are scaling factors on X axis and Y axis respectively. When a point (x,y)T multiplies with M matrix can obtain follows:
Where Sx and Sy are scaling factors on X axis and Y axis respectively. When a point (x,y)T multiplies with M matrix can obtain follows: 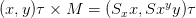 .
.
When Sx=Sy=2, we can understand this transformation matrix can magnify original image by one time. When =1/2, shrink original image by one time. At the same time we can also perform reflection via Scale. When Sx=-1, Sy=1, can implement graphic reflection along Y axis.
Skew
Skew means twist, shear transformation. The simplest transformation matrix to implement it is like this:
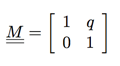
That is a point [x,y]T multiplied with it can obtain:  , that is moving x component of point by an amount proportional to its y component q.
, that is moving x component of point by an amount proportional to its y component q.
Some slightly complex Skews are shown below. Everyone can think about how to implement using transform: skew in CSS3.

Rotation
We can rotate a polygon counterclockwise by θ degrees via the selected matrix below:

We can see from the figure below a point (1,0)T rotated counterclockwise by θ degrees around origin, corner of point (1,0)T moves to point (cosθ,sinθ)T.
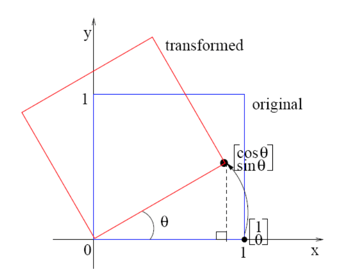
(Written a bit rough later, unify modification when writing next part, flee)
Literature Reference
- Platform Independent Real-Time X3D Shaders and their Applications in Bioinformatics Visualization
- GPGPU PROCESSING IN CUDA ARCHITECTURE
- gpu-accelerated-compositing-in-chrome
- Color Models: RGB, HSV, HSL
- Color Born in Heart: Humanized HSL Model - Tencent CDC
- Color Model Garan no dou
- Understanding Matrix Multiplication - Ruanyifeng’s Network Log
- Matrix Representation of Transformation